Below the Photosphere the Sun Is Best Described as
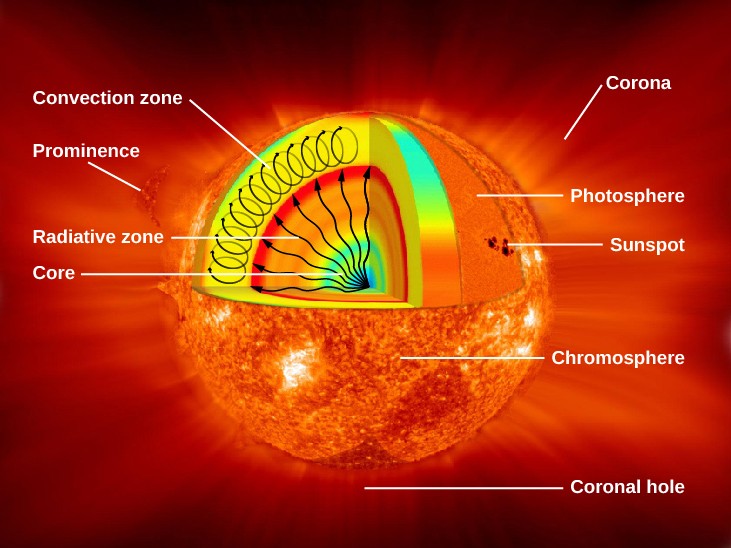
Below the photosphere the sun is best described as. There are various layers in the Sun including the core or core the radiative zone the convection zone the photosphere which emits most of the sunlight the chromosphere and its outer part the corona.
The Structure And Composition Of The Sun Astronomy
For now were going to focus on the photosphere that thin surface layer right above the convective zone.

. Below is a diagram of the Celestial Sphere. Everything below is the Suns interior. The differential rotation of the sun and convection beneath the photosphere What evidence do we have that sunspots are magnetic.
The temperature in the chromosphere varies between about 4000 K at the bottom the so-called temperature minimum and 8000 K at the top 6700 and 14000 degrees F 3700 and 7700 degrees C so in. The sunspot cycle is sometimes describe as lasting 11 years but others prefer to consider it as 22 years. Below are listed some visible colors of stars.
The Sun is most dense somewhere between its surface and its core. A star that has exploded. Over the next few parts well get up close and personal with each one of these parts of the sun.
The lower section of the Suns atmosphere the chromosphere. The density of the photospheres gas is low by Earths standards about 001 as thick as the air we breathe. Rising and sinking gas columns in the photosphere.
We cant see as deeply into the Sun near the edge of its apparent disk and higher cooler material appears darker. A star that is below average in size. When we talk about the temperature luminosity and chemical composition of the Sun what particular layer of the Sun are we talking about.
Red orange yellow blue-white. The spectral lines of sunspots are split by the Zeeman Effect and observations at far ultraviolet show material arched above the suns surface from one sunspot to another. Below the photosphere the gas is denser and hotter that radiates plenty of light.
The Sun is best described as. A The interior region of the Sun in which energy is transferred outward primarily by radiation. The area of the Suns interior immediately below the photosphere is called the convection or convective zone.
The Sun is more dense at its core than at its surface. 5800 k The photosphere is the layer in the suns atmosphere that is dense enough to emit plenty of light but not so dense that the light cant escape. The phenomenon of limb darkening is due to which of the following reasons.
10-1 The photosphere is the visible layer of the Sun. By the outer edge of the radiation zone 20000 km below the photosphere all the photons produced in the suns core have been absorbed. After a very massive stars core runs out of a fuel how does the core get hot enough to ignite the next fusion reaction.
With more and more atoms retaining electrons that can absorb the outgoing radiation the gas in the interior changes from being relatively transparent to being almost totally opaque. Holes in the Suns outer atmosphere make these regions appear darker. However they are still very hot.
The lowest visible layer of a star is the photosphere. The photosphere is the external layer of the Sun which is known as the luminous envelope or the visible layer of the sun from which light as well as heat radiate. - We cannot see through the shimmering gases here.
---The thinness of the photosphere makes the Sun appear to have a distinct edge. Density decreases with altitude from the nucleus. At the center of the diagram is the Earth with the top being the North Pole.
The sun is described as a big star composed mainly of hot hydrogen and helium gas. Whipped around by mega-magnetic field lines are how the prominences and flares on the sun can best be described. Then explain what is happening on the jour.
It is located under the chromosphere and the corona. Which of these best describes the photosphere. A star that is above average in size.
Graph with density The above diagram indicates that. The Sun has about the same density throughout its interior. They are appear dark in visible light because they are much cooler than the rest of the surface of the Sun.
Lowest strata --- 400 km thick. This has an interesting effect on the photosphere. Examine the graph below which shows the journey that a student makes from their homeroom to the cafeteria.
Turbulence below the photosphere seems to flick the magnetic loops back and forth and whip the gas about heating it. When examining a picture of the entire photosphere of the sun we see that. Choose the list that has the colors in proper order from the COOLEST to the HOTTEST.
What layer of the sun moves heat from the radiative layer to the photosphere. Hot material wells up from within the Sun then sinks back down into the. --Convection occurs just below the photosphere.
A loop magnetic fields extnding up through the photosphere. Above the photosphere the gas is less dense and is unable to radiate much light. Because the gas in the chromosphere is ionized and has very low densities it cant resist being accelerated by movements of the magnetic fields.
Chromosphere - The chromosphere is a layer in the Sun between about 250 miles 400 km and 1300 miles 2100 km above the solar surface the photosphere. As Ill describe later the convective zone is a region of rising and sinking gases.

Photosphere Overview Features What Is The Photosphere Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Comments
Post a Comment